Shoulder Anatomy
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body enabling a wide range of movements including, forward flexion, abduction, adduction, external rotation, internal rotation, and 360-degree circumduction.
Thus, the shoulder joint is considered the most insecure joint of the body but the support of ligaments, muscles and tendons function to provide the required stability.
Bones of the Shoulder
The shoulder is a ball and socket joint made up of three bones, namely the humerus, scapula and clavicle.
The end of the humerus or upper arm bone forms the ball of the shoulder joint. An irregular shallow cavity in the scapula called the glenoid cavity forms the socket for the head of the humerus to fit in. The two bones together form the glenohumeral joint, which is the main joint of the shoulder.
The scapula is a flat triangular-shaped bone that forms the shoulder blade. It serves as the site of attachment for most of the muscles that provide movement and stability to the joint. The scapula has four bony processes - acromion, spine, coracoid and glenoid cavity. The acromion and coracoid process serve as places for attachment of the ligaments and tendons.
The clavicle bone or collarbone is an S-shaped bone that connects the scapula to the sternum or breastbone. It forms two joints: the acromioclavicular joint, where it articulates with the acromion process of the scapula, and the sternoclavicular joint where it articulates with the sternum or breast bone. The clavicle also forms a protective covering for important nerves and blood vessels that pass under it from the spine to the arms.
Soft Tissues of the Shoulder
The ends of all articulating bones are covered by smooth tissue called articular cartilage which allows the bones to slide over each other without friction enabling smooth movement. Articular cartilage reduces pressure and acts as a shock absorber during movement of the shoulder bones.
Extra stability to the glenohumeral joint is provided by the glenoid labrum, a ring of fibrous cartilage that surrounds the glenoid cavity. The glenoid labrum increases the depth and surface area of the glenoid cavity to provide a more secure fit for the half-spherical head of the humerus.
Ligaments of the Shoulder
Ligaments are the thick strands of fibers that connect one bone to another. The ligaments of the shoulder joint include:
- Coraco-clavicular ligaments: These ligaments connect the collarbone to the shoulder blade at the coracoid process.
- Acromio-clavicular ligament: This connects the collarbone to the shoulder blade at the acromion process.
- Coraco-acromial ligament: It connects the acromion process to the coracoid process.
- Glenohumeral ligaments: A group of 3 ligaments that form a capsule around the shoulder joint, and connect the head of the arm bone to the glenoid cavity of the shoulder blade. The capsule forms a water-tight sac around the joint. Glenohumeral ligaments play a very important role in providing stability to the otherwise unstable shoulder joint by preventing dislocation.
Muscles of the Shoulder
The rotator cuff is the main group of muscles in the shoulder joint and is comprised of 4 muscles. The rotator cuff forms a sleeve around the humeral head and glenoid cavity, providing additional stability to the shoulder joint while enabling a wide range of mobility.
The deltoid muscle forms the outer layer of the rotator cuff and is the largest and strongest muscle of the shoulder joint.
Tendons of the Shoulder
Tendons are strong tissues that join muscle to bone allowing the muscle to control the movement of the bone or joint. Two important groups of tendons in the shoulder joint are the biceps tendons and rotator cuff tendons.
Bicep tendons are the two tendons that join the bicep muscle of the upper arm to the shoulder. They are referred to as the long head and short head of the bicep.
Rotator cuff tendons are a group of four tendons that join the head of the humerus to the deeper muscles of the rotator cuff. These tendons provide more stability and mobility to the shoulder joint.
Nerves of the Shoulder
Nerves carry messages from the brain to muscles to direct movement (motor nerves) and send information about different sensations such as touch, temperature and pain from the muscles back to the brain (sensory nerves). The nerves of the arm pass through the shoulder joint from the neck.
These nerves form a bundle at the region of the shoulder called the brachial plexus. The main nerves of the brachial plexus are the musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, ulnar and median nerves.
Blood vessels of the Shoulder
Blood vessels travel along with the nerves to supply blood to the arms. Oxygenated blood is supplied to the shoulder region by the subclavian artery that runs below the collarbone. As it enters the region of the armpit, it is called the axillary artery and further down the arm, it is called the brachial artery. The main veins carrying de-oxygenated blood back to the heart for purification include:
- Axillary vein: this vein drains into the subclavian vein
- Cephalic vein: this vein is found in the upper arm and branches at the elbow into the forearm region. It drains into the axillary vein.
- Basilic vein: this vein runs opposite the cephalic vein, near the triceps muscle. It drains into the axillary vein.
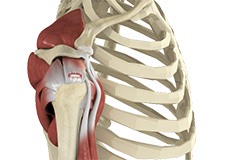
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff is a group of tendons in the shoulder joint that provides support and enables a wide range of motion. A major injury to these tendons may result in rotator cuff tears.
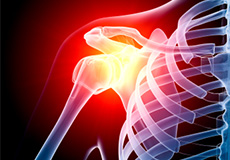
Shoulder Pain
Pain in the shoulder may suggest an injury, which is more common in athletes participating in sports such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting. The injuries are caused due to the over usage or repetitive motion of the arms.
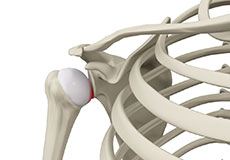
Subluxation
The shoulder is a highly mobile ball and socket joint. The ball of the upper arm bone (humerus) is held in place at the socket (glenoid) of the shoulder blade (scapula) by a group of ligaments.
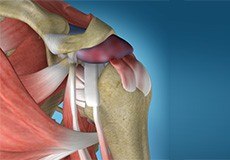
Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder impingement is the inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint. It is one of the most common causes of pain in the shoulder. Shoulder impingement is also called swimmer’s shoulder, tennis shoulder or rotator cuff tendinitis.
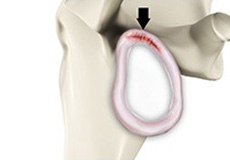
SLAP Tears
The term SLAP (superior –labrum anterior-posterior) lesion or SLAP tear refers to an injury of the superior labrum of the shoulder.
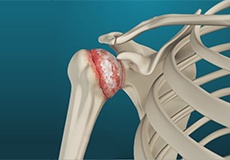
Arthritis of the Shoulder
The term arthritis literally means inflammation of a joint but is generally used to describe any condition in which there is damage to the cartilage. Damage of the cartilage in the shoulder joint causes shoulder arthritis.
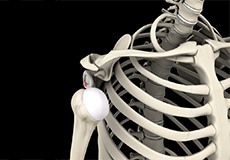
Shoulder Instability
Shoulder instability is a chronic condition that causes frequent dislocation of the shoulder joint.
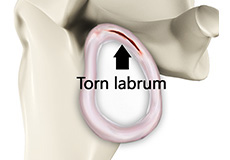
Shoulder Labral Tear
Traumatic injury to the shoulder or overuse of the shoulder (throwing, weightlifting) may cause the labrum to tear. In addition, aging may weaken the labrum leading to injury.
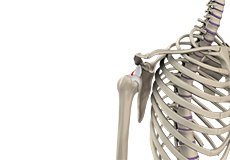
Shoulder Dislocation
Sports that involve overhead movements and repeated use of the shoulder at your workplace may lead to sliding of the upper arm bone from the glenoid. The dislocation might be a partial dislocation (subluxation) or a complete dislocation causing pain and shoulder joint instability.
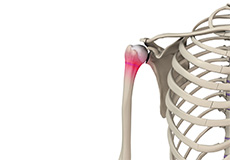
Little League Shoulder
Little league shoulder is an injury to the growth plate of the upper arm bone at the shoulder joint of children. It is an overuse injury caused by repeated pitching or throwing, especially in children between the ages of 10 to 15 years.
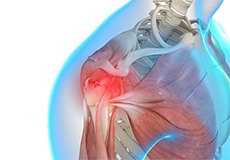
Shoulder Trauma
Shoulder injuries most commonly occur in athletes participating in sports such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting. The injuries are caused due to the over usage or repetitive motion of the arms.
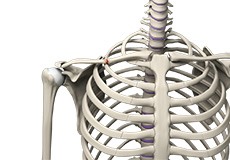
Clavicle Fracture
The break or fracture of the clavicle (collarbone) is a common sports injury associated with contact sports such as football and martial arts, as well as impact sports such as motor racing.

Baseball and Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries in baseball players are usually associated with pitching. While this overhand throwing activity can produce great speed and distance for the ball, when performed repeatedly, can place a lot of stress on the shoulder.
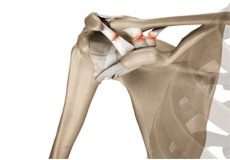
Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people. AC joint osteoarthritis affects the tissue covering the ends of bones (cartilage) in the AC joint of the shoulder.

Treatment of Throwing Injuries of the Shoulder
Throwing injuries of the shoulder are injuries sustained as a result of trauma by athletes during sports activities that involve repetitive overhand motions of the arm as in baseball, American football, volleyball, rugby, tennis, track and field events, etc.
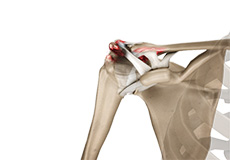
Acromioclavicular (AC) Arthritis
The acromioclavicular joint is part of the shoulder joint. It is formed by the union of the acromion, a bony process of the shoulder blade, and the outer end of the collar bone or clavicle.
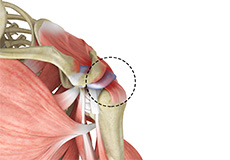
Rotator Cuff Pain
The rotator cuff consists of a group of tendons and muscles that surround and stabilize the shoulder joint. These tendons allow a wide range of movement of the shoulder joint across multiple planes. Irritation or injury to these tendons can result in rotator cuff pain.
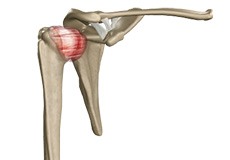
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by pain and loss of motion in the shoulder joint. It is more common in older adults aged between 40 and 60 years and is more common in women than men.
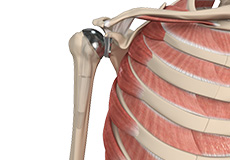
Total Shoulder Replacement
Total shoulder replacement surgery is performed to relieve these symptoms. In this surgery, the damaged articulating parts of the shoulder joint are removed and replaced with artificial prostheses.
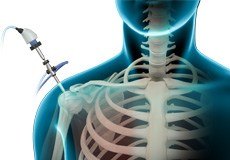
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedure performed for joint problems. Shoulder arthroscopy is performed using a pencil-sized instrument called an arthroscope.
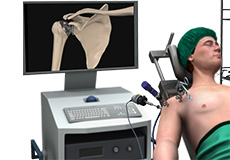
Minimally Invasive Shoulder Joint Replacement
Shoulder joint replacement is a surgical procedure that replaces damaged bone surfaces with artificial humeral and glenoid components to relieve pain and improve functional ability in the shoulder joint.
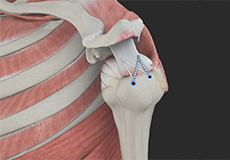
Rotator Cuff Repair
The rotator cuff is a group of tendons and muscles in the shoulder joint providing support and enabling a wider range of shoulder motion. Injury to the rotator cuff may occur due to pressure on the rotator cuff from part of the shoulder blade (scapula).
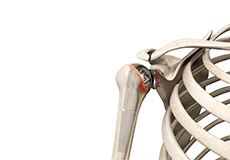
Revision Shoulder Replacement
Total shoulder replacement is the replacement of the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) and the glenoid cavity (cavity of the shoulder blade) into which the humerus fits, with artificial prostheses to relieve pain, swelling, and stiffness caused due to damage of cartilage at the articulating surfaces.
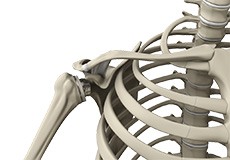
Reverse Shoulder Replacement
Conventional surgical methods such as total shoulder joint replacement have been shown to be significantly ineffective in the treatment of rotator cuff arthropathy.
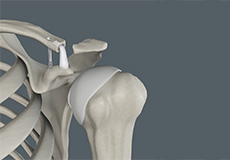
Acromioclavicular Joint (AC) Joint Reconstruction
The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is one of the joints present within your shoulder. It is formed between a bony projection at the top of the shoulder blade (acromion) and the outer end of the clavicle (collarbone).
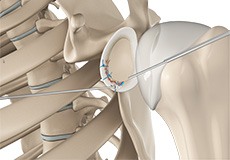
Arthroscopic Bankart Repair
The labrum can sometimes tear during a shoulder injury. A specific type of labral tear that occurs when the shoulder dislocates is called a Bankart tear.
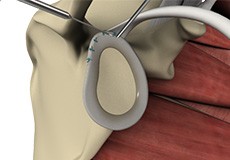
SLAP Repair
A SLAP tear can be treated through an arthroscopic surgical procedure called a SLAP repair.

Arthroscopic Acromioplasty
Acromioplasty is the surgical removal of a small part of the surface of the acromion (bony process on your shoulder blade). The shoulder joint is made up of a ball and socket joint, where the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) articulates with the socket of the scapula (shoulder blade), which is called the glenoid.
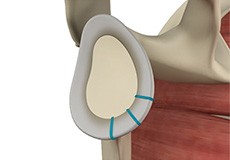
Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction
Traumatic injury to the shoulder or overuse of the shoulder by excessive throwing or weightlifting can cause a labral tear. In addition, the aging process may weaken the labrum, leading to injury secondary to wear and tear.
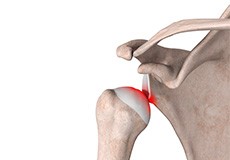
Shoulder Stabilization
Shoulder instability is a chronic condition that causes the frequent dislocation of the shoulder joint. A dislocation occurs when the end of the humerus (the ball portion) partially or completely dislocates from the glenoid (the socket portion) of the shoulder.
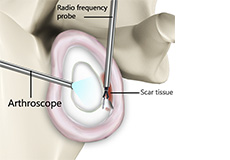
Capsular Release
A capsular release of the shoulder is surgery performed to release a tight and stiff shoulder capsule, a condition called frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitis. The procedure is usually performed arthroscopically through keyhole-size incisions.
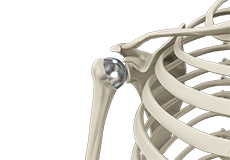
Shoulder Resurfacing
The shoulder is an active joint is prone to injuries and may also get affected by conditions such as arthritis, which results in impaired functioning and related discomfort.

Acromioclavicular Joint (AC) Joint Reconstruction
The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is one of the joints present within your shoulder. It is formed between a bony projection at the top of the shoulder blade (acromion) and the outer end of the clavicle (collarbone).
Shoulder Fracture Care
A break in the bone that makes up the shoulder joint is called a shoulder fracture. The clavicle (collarbone) and end of the humerus (upper arm bone) closest to the shoulder are the bones that usually are fractured.





